|
Red Cell Distribution Width (RDW)
The RDW is an index of the variation in cell volume within the red cell population.
It is a parameter provided by both impedance and flow cytometric analyzers.
Mathematically, it is the coefficient of variation, i.e.,
RDW = (Standard deviation of red cell volume
÷ mean cell volume) x 100
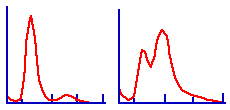
Red cell populations with higher than normal RDW are termed heterogenous;
those with normal RDW are homogeneous. For example, increased
numbers of reticulocytes will cause an increased RDW. In some instances,
the RDW is the first test result to increase with changes in red cell
population sizes. For example, in early iron deficiency, there are only
low numbers of microcytic red blood cells. This will increase the standard
deviation and the RDW, but the mean cell volume is unchanged because
there are insufficient numbers of microcytic cells to change the mean
volume.
| |
Which of these red cell histograms represents the
population with the greater RDW? (Click within the
image for explanation)
|
Last Updated: June 2000
|