
A 78 year old man is brought into the emergency department for decreased appetite and "altered mental status". On exam he is responsive to strong stimuli, has dry mucous membranes, flat neck veins, sacral decubitus ulcers and appears to be moving all extremities and facial muscles without deficits. His vitals are T=97.0, BP=90/50, HR=130, RR-14. You draw labs and obtain IV access. His labs return and he is found to have the following values:
Na=160 K=5.5 Cl=95 HCO3=32 Glucose=140
The patient weighs 70 kg. What is this patients free water deficit:
You would next:
A 22 year old woman comes to see you in the clinic because she has stopped having menstrual periods. She had been regular since age 14 with her periods beginning midmonth and lasting 4-5 days. She has recently become sexually active and is not practicing any form of birth control. She also started jogging and has headaches from time-to-time. Please rank the following 4 conditions from MOST likely to Least likely etiology:
A gentleman presents to your ambulatory clinic complaining of "heart burn." He has had these symptoms in the past 2 months, relieved with Maalox, Mylanta or TUMS. He comes to you for advice on how to prevent this. Which of the following items would you tell him to avoid for his gastroesophagel reflux disease: (answer yes or no to each)
A 20 year old sexually active women presents to your clinic with polyuria, dysuria without fevers, chills, nausea without vomiting. This is the first time she has ever felt this way and thinks she has "the flu". In the office you "dip" her urine and it has the following characteristics:
Yellow, 1.020, 6.0, 2+protein, +nitrites, + leuk esterase, 3-5 RBC's, many WBC's, many bacteria, no epithelial cells.
You would next do the following:
A 40 year old man presents to your office with a 2 month history of polyuria, nocturia, polydipsia, polyphagia and a 30 pound weight loss despite having a "great" appetite. Eight hours prior he had drank a milkshake. A FSG in the office is 250 and a urine dipstick shows 4+ glucose only. His office visit height and weight were 5 foot 7 inches and 150 lbs. What would you do next:
A 32 year old white woman presents to the emergency department with sudden onset of a painful right knee. The pain is associated with fever, chills and immobility of the knee. She is sexually active. A knee joint aspiration reveals the following:
Turbid, yellowish-red fluid. WBC=105,000 with N90 L10, Glucose=10 mg/dL, Protein=150 mg/dL. A gram stain of the fluid reveals the following:

You would give this patient:
A 70 year old man presents to the E.D. with fever, chills, headaches and confusion. You perform a lumbar puncture and the fluid reveals the following:
Opening pressure=16 cm H2O
WBC=200 P20 L80; RBC=0
Glucose=40 mg/dL (serum=110) Protein=90 mg/dL
The gram stain of the CSF shows the following:

You would then admit the patient to the hospital and treat with:
A 30 year old woman presents with sudden, progressive "blurring" of vision in the left eye only. You dilate her eyes and do a ophthamologic examination. Her right eye is normal. The left eye shows the following:
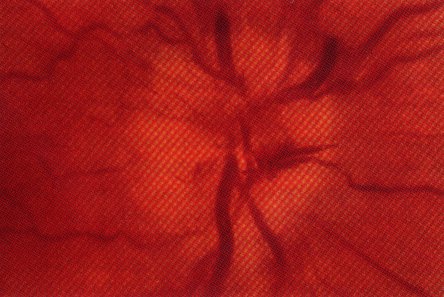
You would then do the following:
A 25 year old woman with a history of asthma presents to the emergency department with a one day history of gradual shortness of breath requiring her to use her nebulizer treatments at home more frequently. She presents to the E.D. with wheezing, tachypnea with a respiratory rate of 40, diaphoresis, unable to speak 1 full sentence and pleuritic chest pain. A peak flow meter reading registers a P.E.F. = 150cc/sec. You should treat her with all the following EXCEPT:
7.35/40/80/O2sat=98%
You should now: