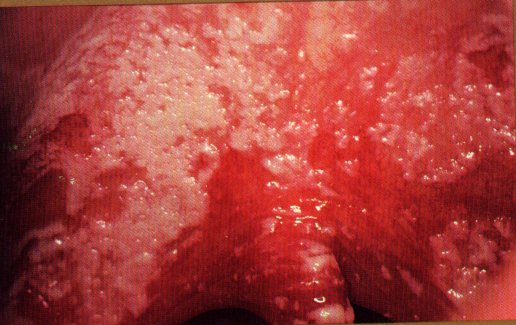
A patient with HIV on antiretroviral therapy (AZT,3TC,Crixivan) presents with a one week history of dysphagia. This person has never had this before and is able to keep most food down with some difficulties. An oral examination reveals the following lesions which scrape off with a tongue blade:

You would treat this condition with:
A 40 year old woman presents with a 2 year complaint of flushing, diarrhea and occasional shortness of breath. Below is a before and after picture of the patient during a flushing episode:
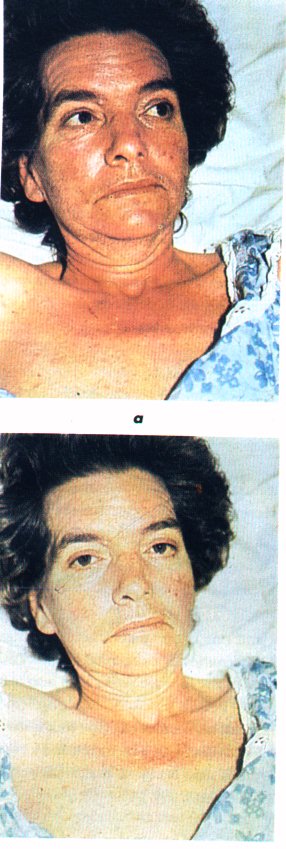
Flushing is characteristic of all these conditions EXCEPT:
This particular lady has wheezing with her flushing episodes, as well as diarrhea. On examination she also has pulsatile hepatomegaly and a 2/6 systolic ejection murmur along the left sternal border that increases with respiration. She also has associated paroxysmal hypotension during a typical flushing episode. The appropriate diagnosis can be made by which of the following:
This patient is seen in your clinic complaining of severe headache, some shortness of breath and decreased urine output:

His blood pressure is 210/110 and a urine dipstick reveals hematuria and proteinuria. You admit him to the hospital where he is found to be in mild pulmonary edema. His blood work is most notable for a BUN=80 and a Creatinine=6.5. Which agent would be the best to treat this conditon:
A 72 year old white woman presents to the ED complaining of left-leg discoloration, pain, and swelling which developed over several hours. The patient has a history of bilateral leg swelling of 2-3 months' duration, for which she had been wearing compression stockings. She noticed some mild reddish-blue discoloration at the top of her left stocking associated with a burning-itching sensation. She then removed the stockings and noticed that a large area of her left upper leg was reddish-blue with small blisters and markedly more swollen. The patient denies any fever, trauma, or bites. Doppler ultrasonography of her left leg two weeks prior had yielded normal results.
PHYSICAL EXAMINATION:
The patient is alert, appears pale and anxious, and is in moderate discomfort from pain in her left leg. Her vital signs are temperature 97.8 degrees F (rectal), pulse 73 beats/min, blood pressure 113/59 mm of Hg, and respirations 18 breaths/minute. The results of her HEENT, cardiovascular, respiratory, abdominal, and neurological exams are normal. Her left leg is tender to palpation without crepitus. Pitting edema extends the entire length of the leg with a reddish- blue discoloration. Numerous small vesicles are also noted with three, 3- 5 cm hemorrhagic bullae on the medial thigh.
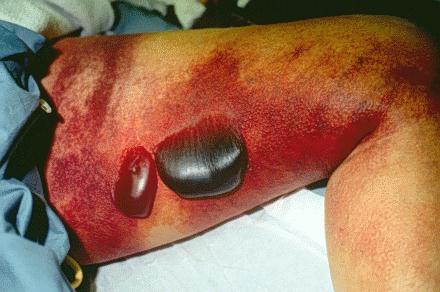
The patient also complained of a burning-itching like pain in her left leg with palpation. Neurological exam is normal in the extremity. Pulses are normal in the affected leg, however capillary refill time is three seconds. No adenopathy is present.
LABORATORY:
The white blood cell count is 8,700 with a normal differential, a Hb of 10.7 g/L, a hematocrit of 32.8%, and 168,000 platelets. The level of sodium is 130 mmol/L, potassium 3.5 mmol/L, chloride 101 mmol/L, carbon dioxide 14 mmol/L. The serum glucose is 110, BUN is 15, and creatinine is 2.0. Prothrombin time is 23.4 seconds, and partial thromboplastin time is 29.8 seconds. Fibrinogen and fibrin split products are normal. Chest, left leg x-rays and repeat left leg Doppler ultrasonogram are normal.
A gram stain of the wound exudate reveals the following:
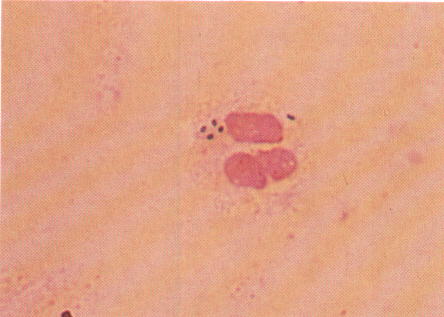
The most appropriate therapy for this patient is:
A 42 year old woman has bilateral ankle edema of recent onset. On examination, her JVP (jugular venous pressure) is 6 cm H2O and hepatojugular reflex is negative. All of the following should be considered in the differential of diagnosis of the woman's ankle edema EXCEPT:
Which of the following case histories would most likely be associated with the urinary sediment depicted below?
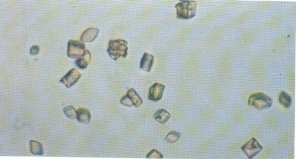
A 60-year-old mildly obese woman complains of a very bothersome burning pain on the anterolateral aspect of her right thigh from the groin almost as far distally as the knee. Examination shows reduction of sensation to touch and pinprick in the affected area. There is no loss of muscle strength, and reflexes are normal. The most likely diagnosis is:
Known consequences of asbestos exposure include all of the following EXCEPT: