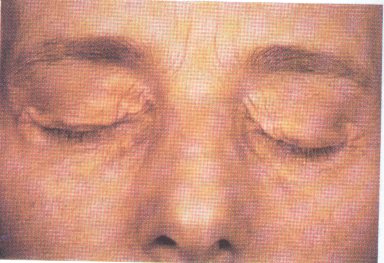
A 50-year-old woman notices the development of these fleshy lesions on her eyelids.

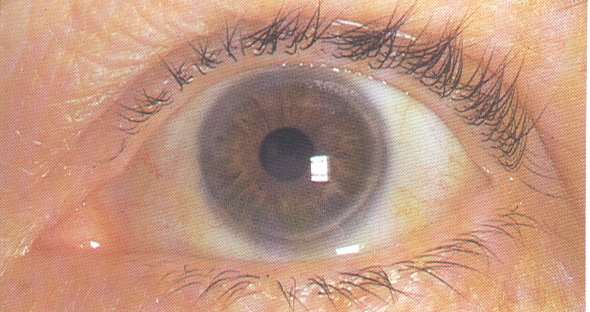
You continue with your physical exam and also note the following:
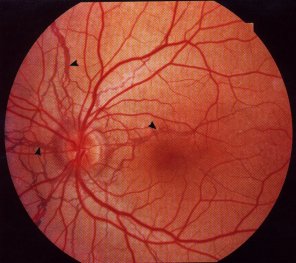
Still interested in her eyes, you then proceed with a dilated fundoscopic exam and see the following in both of her eyes. She denies any decrease in her visual acuity:
You begin to follow her in your clinic. As her primary care physician what are you most interested in following:
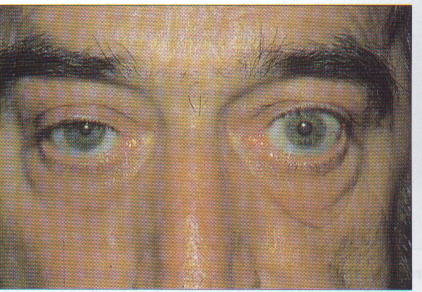
A 65 year-old man with a history of hypertension and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease secondary to cigarette smoking presents to a physician in the clinic because his wife thought "he looked different". He also has had the development of right back and shoulder pain. This is a picture of his face:
The first step in the workup should be:
A 48-year-old woman presents to the office with a 3-week history of progressive shortness of breath. She does not drink or smoke. She had been in generally good health until she began losing weight about 2 months ago. One week ago she began vomiting after meals. Her family history is unremarkable. She is afebrile, and on chest examination she has dullness to percussion, decreased breath sounds without egophany at the right base. Her abdominal exam is unremarkable with no tenderness to palpation, no hepatosplenomegaly and normal bowel sounds. Wisely, you decide to get a chest x-ray:
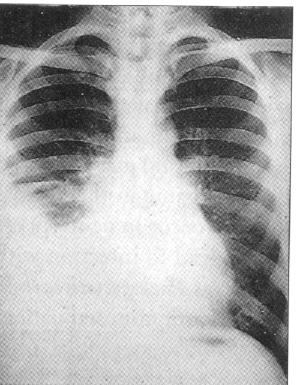
You proceed with some laboratory studies:
Serum values:
Hct=37% WBC=8,700 N67 L20 M10 E3 Amylase=86 Total protein=6.2 LDH=210
Thoracentesis values:
RBC=110,000 WBC=1,100 Mono70 Neut20 Meso10 Protein=4.3 LDH=300 Amylase=450 pH=7.43 Cytology=negative
The most likely diagnosis is:
A 45-year-old man presents to you with the following leg ulcer of the lateral calf:
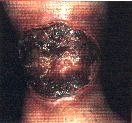
He has had this lesion going on 3-4 months. It is minimally painful and has failed soaking in water, wrapping it with bandages, cleaning with hydrogen peroxide or applying bacitracin. Being the astute clinician you do a complete history and on review of systems you also get a history of arthralgias and occasional bloody diarrhea over the past few years. On exam, he does have some evidence of synovitis in diffuse joints but otherwise the physical exam is unremarkable.
The most likely diagnosis is
You are seeing a 43-year-old woman for a health maintenance checkup. She is generally healthy with no history of coronary heart disease. She does have a positive family history for myocardial infarction in a 53-year-old brother and 59-year-old sister. She smokes 1 pack of cigarettes a day but is unwilling to consider stopping at this time. At a recent visit, you obtained a lipid profile which revealed an LDL=140 with a normal HDL. This is consistent with a previous measurement made one year prior.
The best strategy for the next phase of management for this woman is:
A 77-year-old woman presents to the emergency room with sudden onset of severe chest pain radiating to her back just a few minutes after lifting a carton of books. Her past medical history is noteworthy for chronic hypertension and mild obesity. Her only medications include a daily aspirin and a thiazide diuretic, both of which she infrequently takes. On examination she is anxious and in severe pain. Her heart rate is 89/min and her blood pressure is 175/105 mm Hg. On examination her chest, heart, abdomen and extremities are normal. There is no point of tenderness over the chest or back. All pulses are full and bowel sounds are normal.
Her Hgb=11, BUN=18 mg/dL, creatinine=1.1 mg/dL.
Two EKG's are performed 10 minutes apart and both look like this:

She is given sublingual nitroglycerin with a decrease in blood pressure to 150/90 mm Hg and her heart rate=90. After the nitroglycerin she states her chest pain is still intense and is rated a 9 on a scale of 1-10 (1 = minimal, 10 = worst pain in my life).
You then get a chest x-ray:
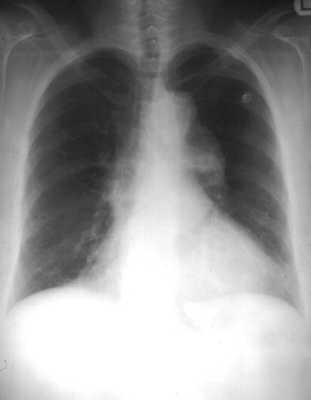
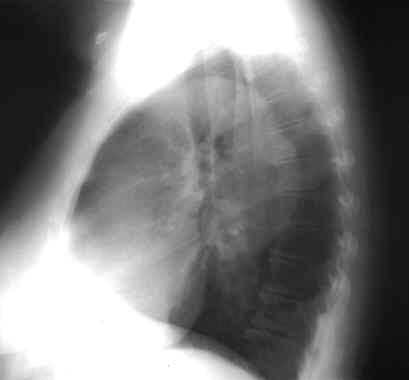
Which one of the following is the most appropriate next step in managing this patient?
A 55-year-old woman with metastatic breast cancer to the bone presents with fever (temperature of 101.8 F). She received palliative treatment with paclitaxel chemotherapy 10 days ago. Her only symptoms is a painful vesicular rash along the right thorax. Physical examination shows an acutely ill-appearing woman with a normal oropharynx, clear chest, negative cardiac and abdominal examinations and a vesicular rash:
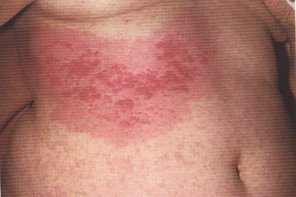
Laboratory studies reveal a Hgb=11 g/dL, WBC=1.1, Platelets=30,000. All other chemistries, liver function tests, urinanalysis and chest x-ray are within normal limits. Blood cultures are obtained.
Which of the following is the most appropriate intervention at this time?
A colleague asked your opinion of the heart sounds of one of his patients. On auscultation, you hear regular rate and rhythm. S1 is normal sounding and S2 is split - increased with inspiration and is decreased but does not disappear with exhalation. No murmurs are heard.
Which of the following ECG's is consistent with the patients heart sounds?
A 33 year-old married woman has a blood pressure in the 150-172/92-104 mm Hg range on multiple clinic visits. Her medical history is unremarkable. She does not take any medications and is not using oral contraceptives. She has a family history of hypertension and her mother suffered a myocardial infarction at age 54.
Physical examination shows a blood pressure of 162/98 mm Hg, pulse of 76/min, symmetrical pulses, minimal narrowing of retinal arteries, prominent S4 gallop and no abdominal bruits. Basic chemistry tests and urinalysis are normal; fasting cholesterol is 248 mg/dL.
Which one of the following medications would be the LEAST appropriate for this patient?
A 55-year old man has chronic lymphocyte leukemia. He is currently in remission and not taking any medication. While in remission, he had an acute episode of angioedema of his face and tongue. Intubation was required and the swelling slowly subsided over 3 days. Since this episode he has had more attacks of angioedema of his hands, face, and tongue. They do not respond to epinephrine or antihistamines and resolve slowly with prednisone. He has never had urticaria and there is no family history of angioedema.
Which laboratory test is most likely to be diagnostic in this case?